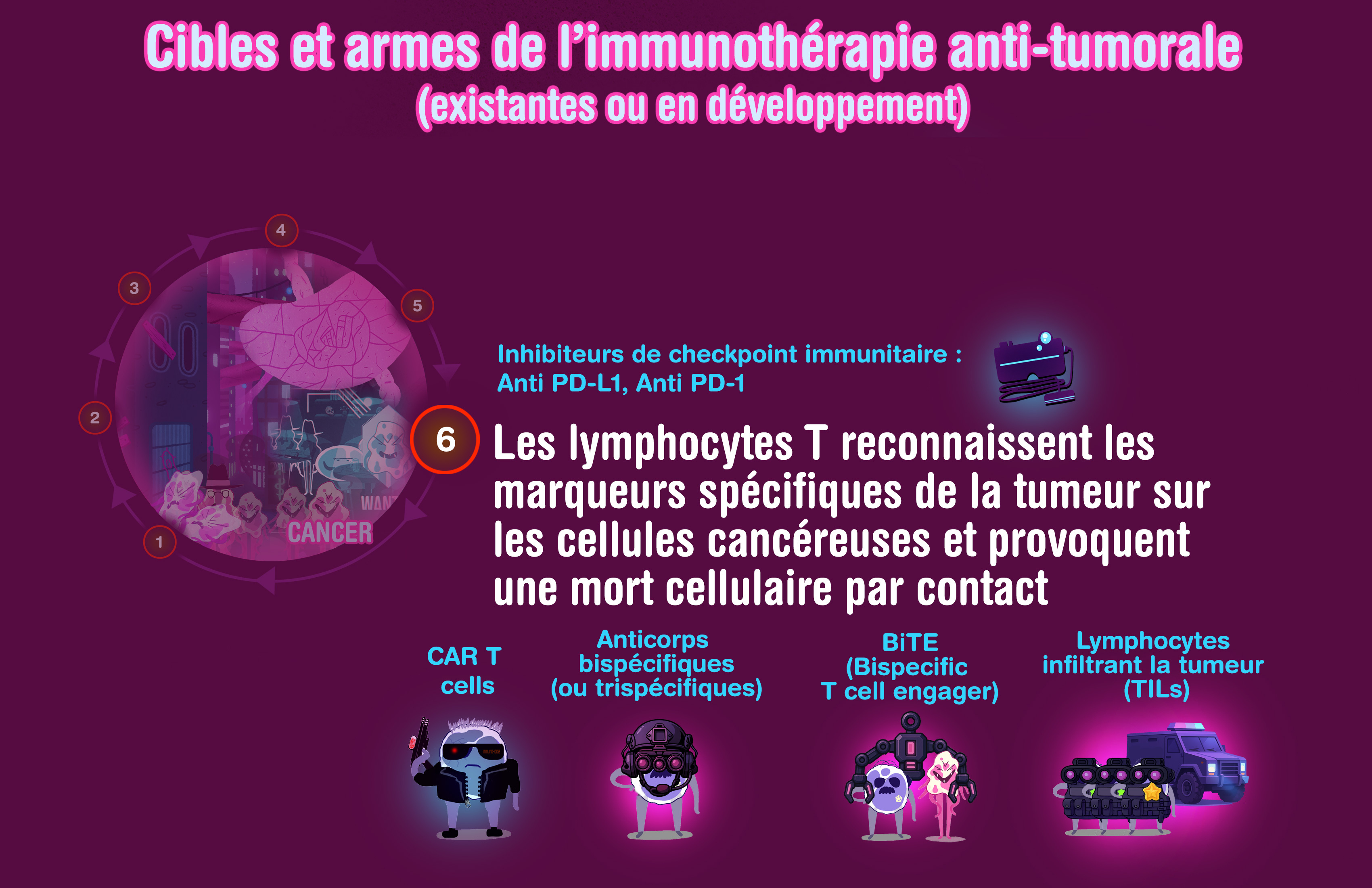
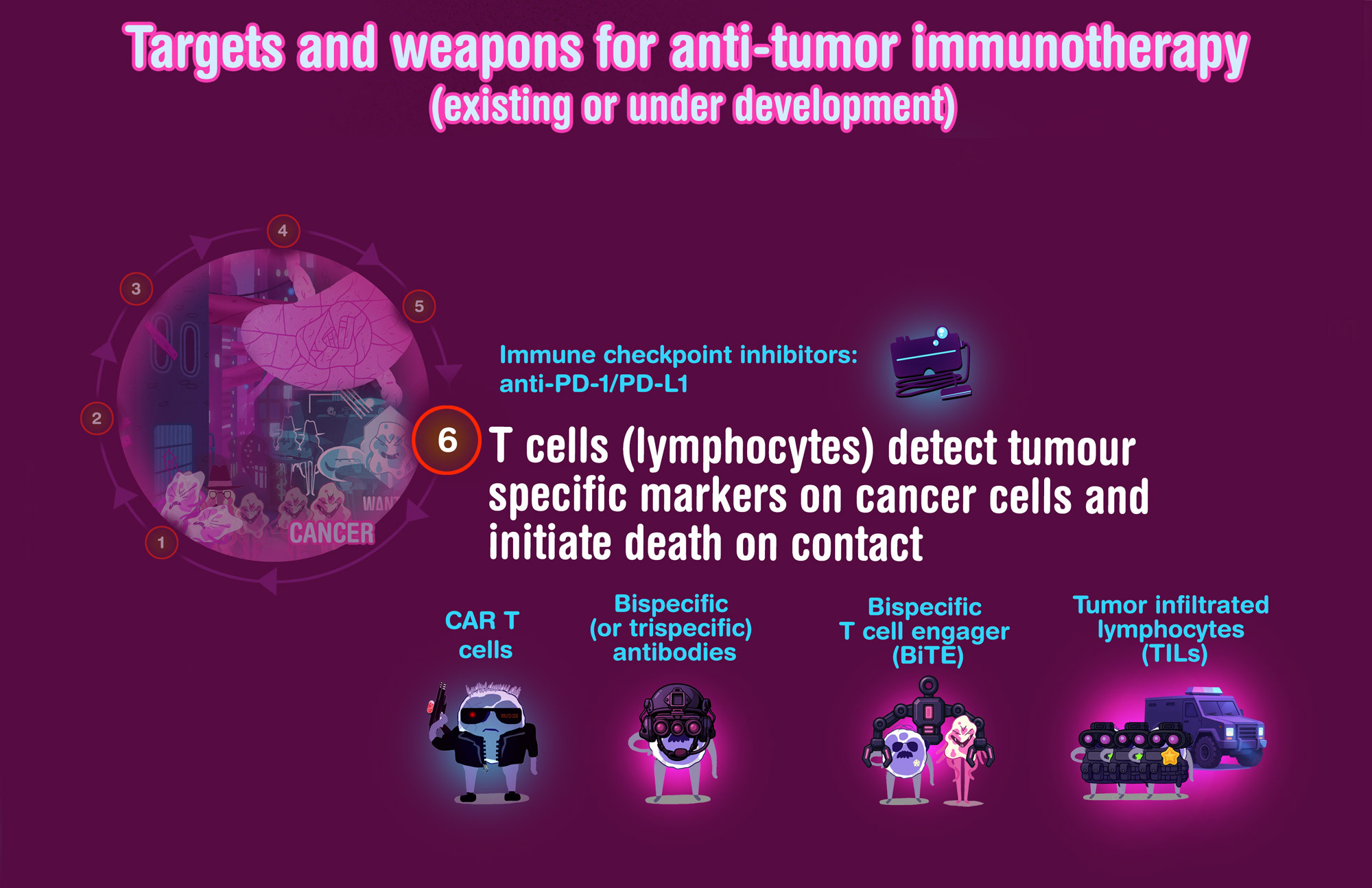
Immunotherapy (figures)
For a better understanding of anti-tumor immunotherapy, here are a few figures of how it works. For further explanations, please contact your doctor.
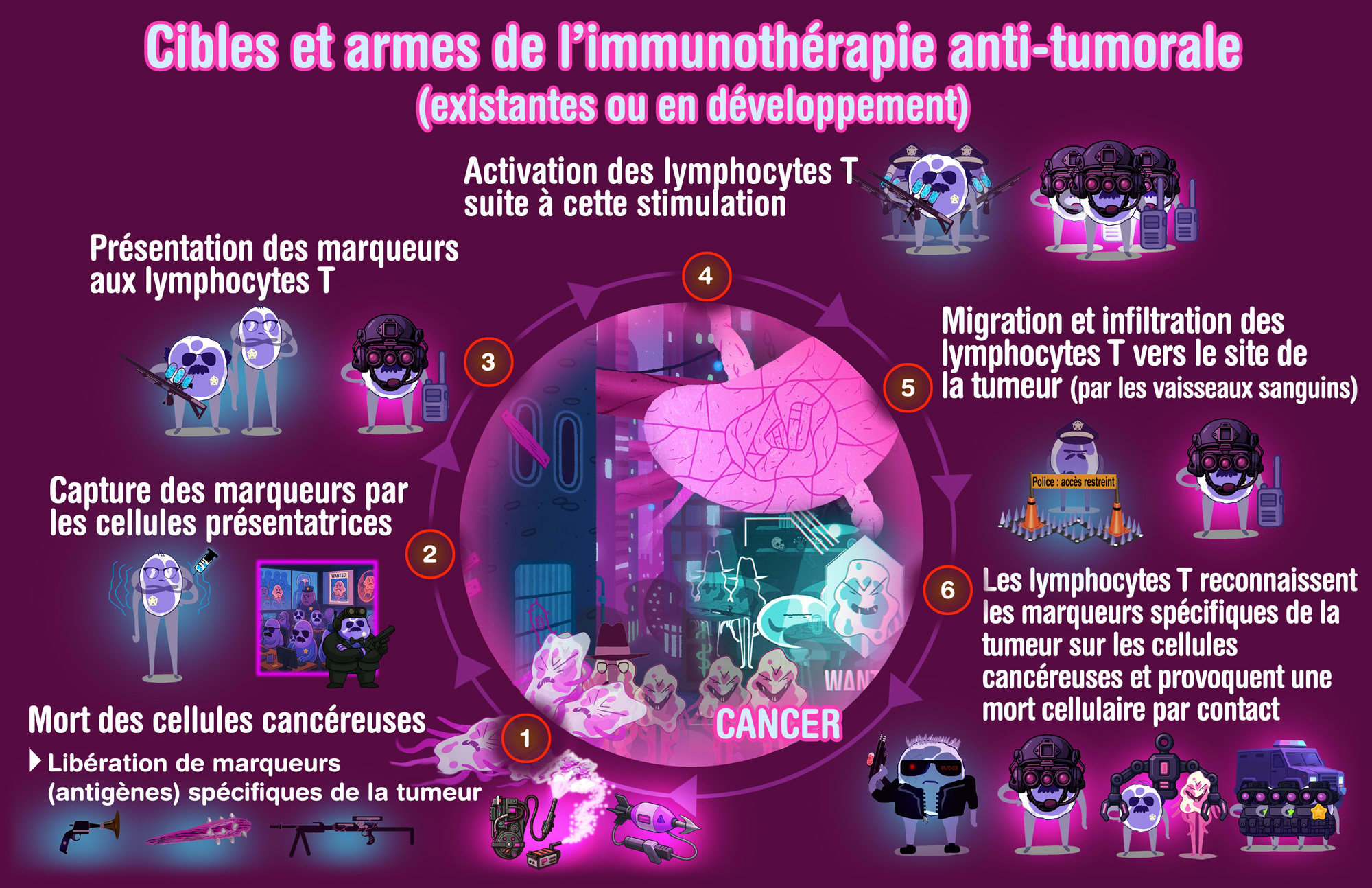
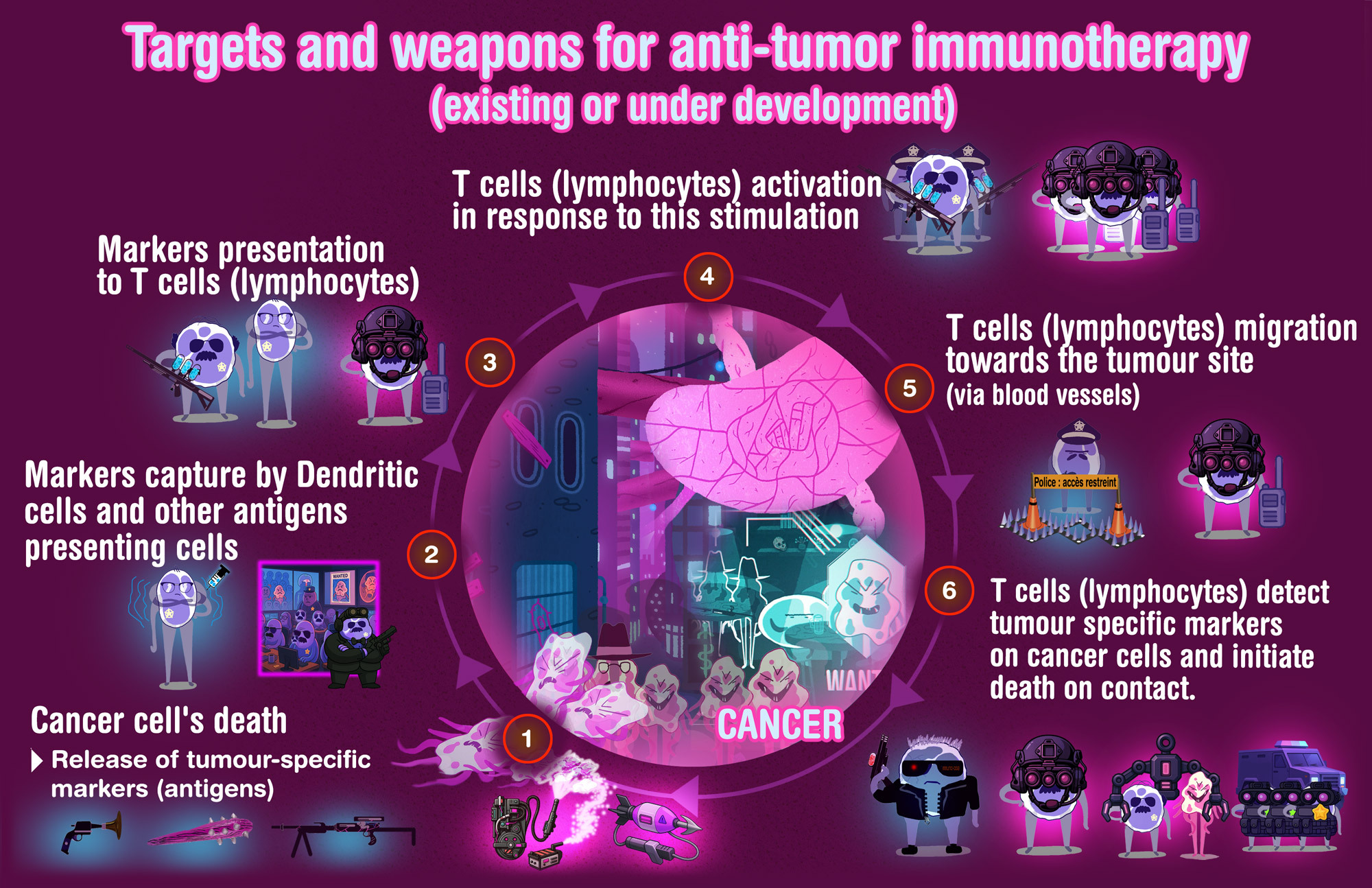
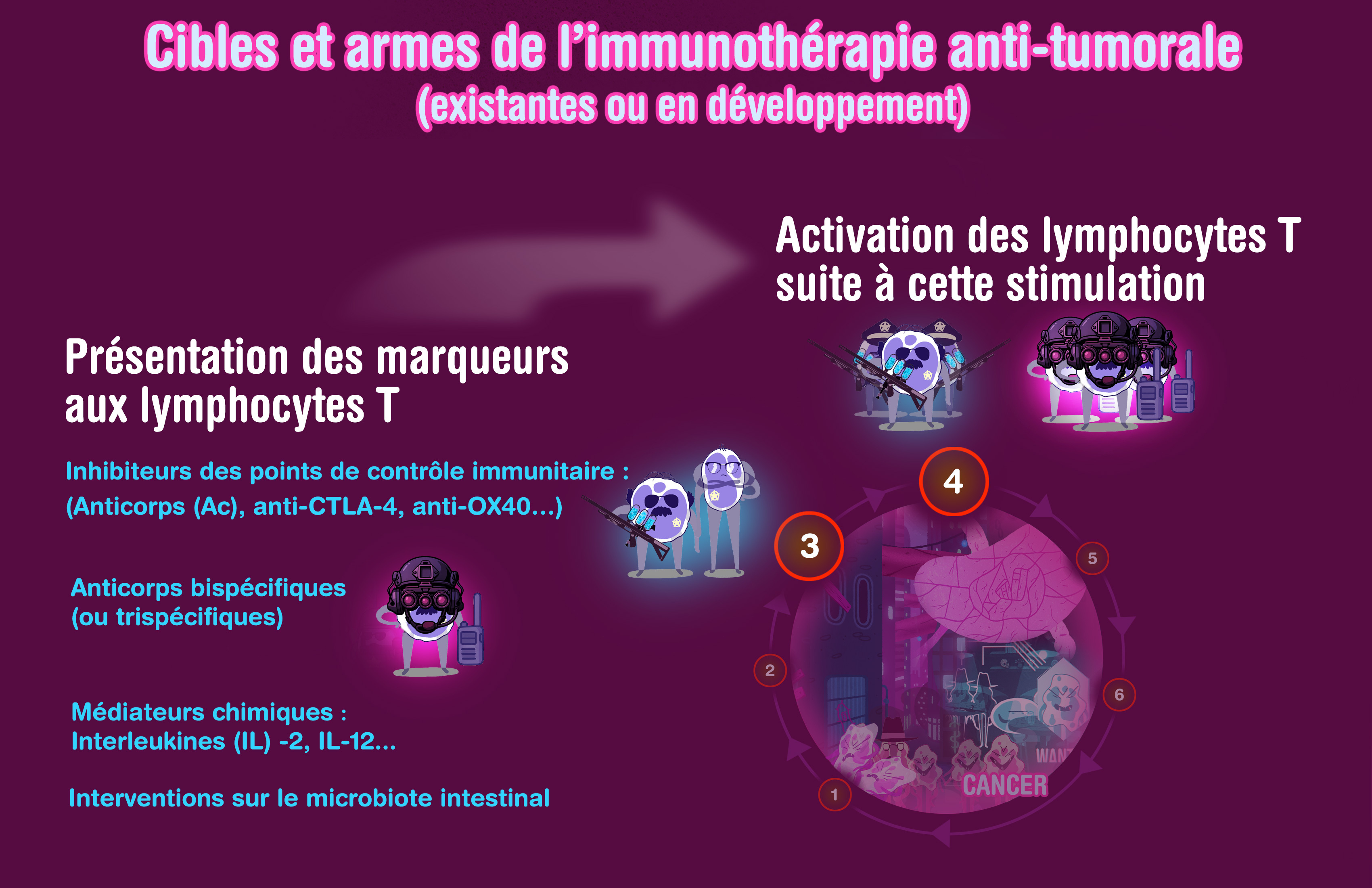
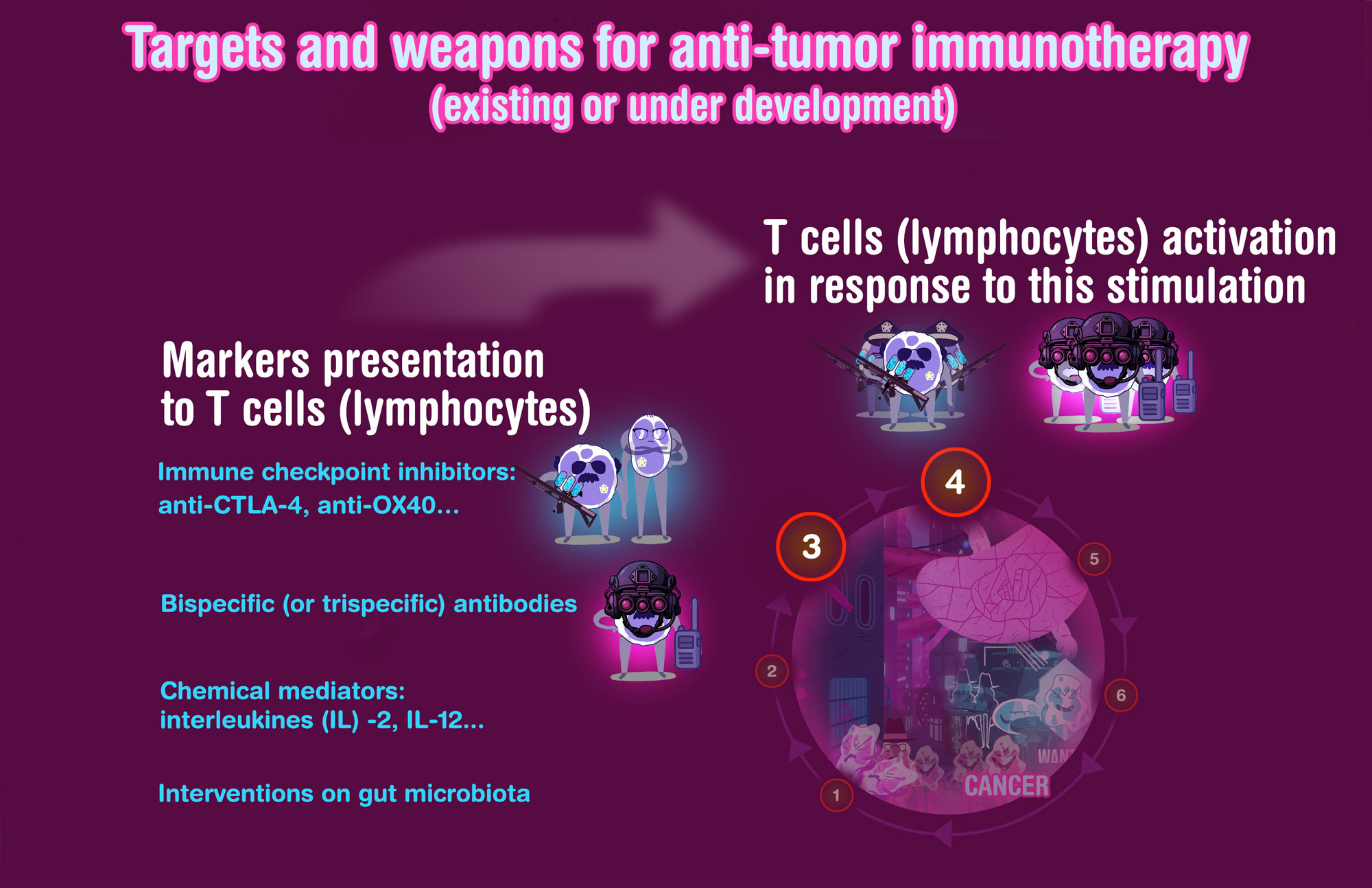
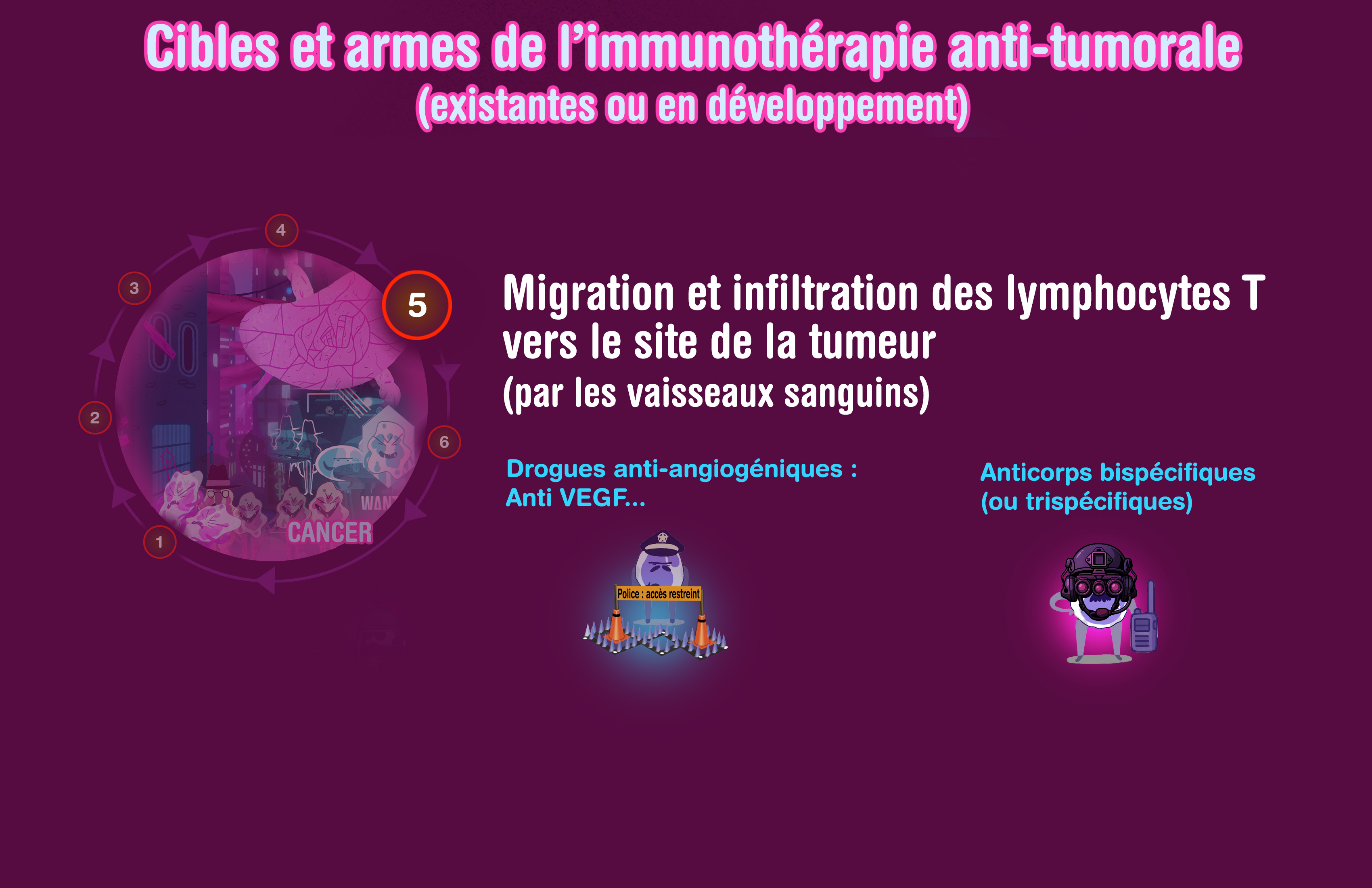
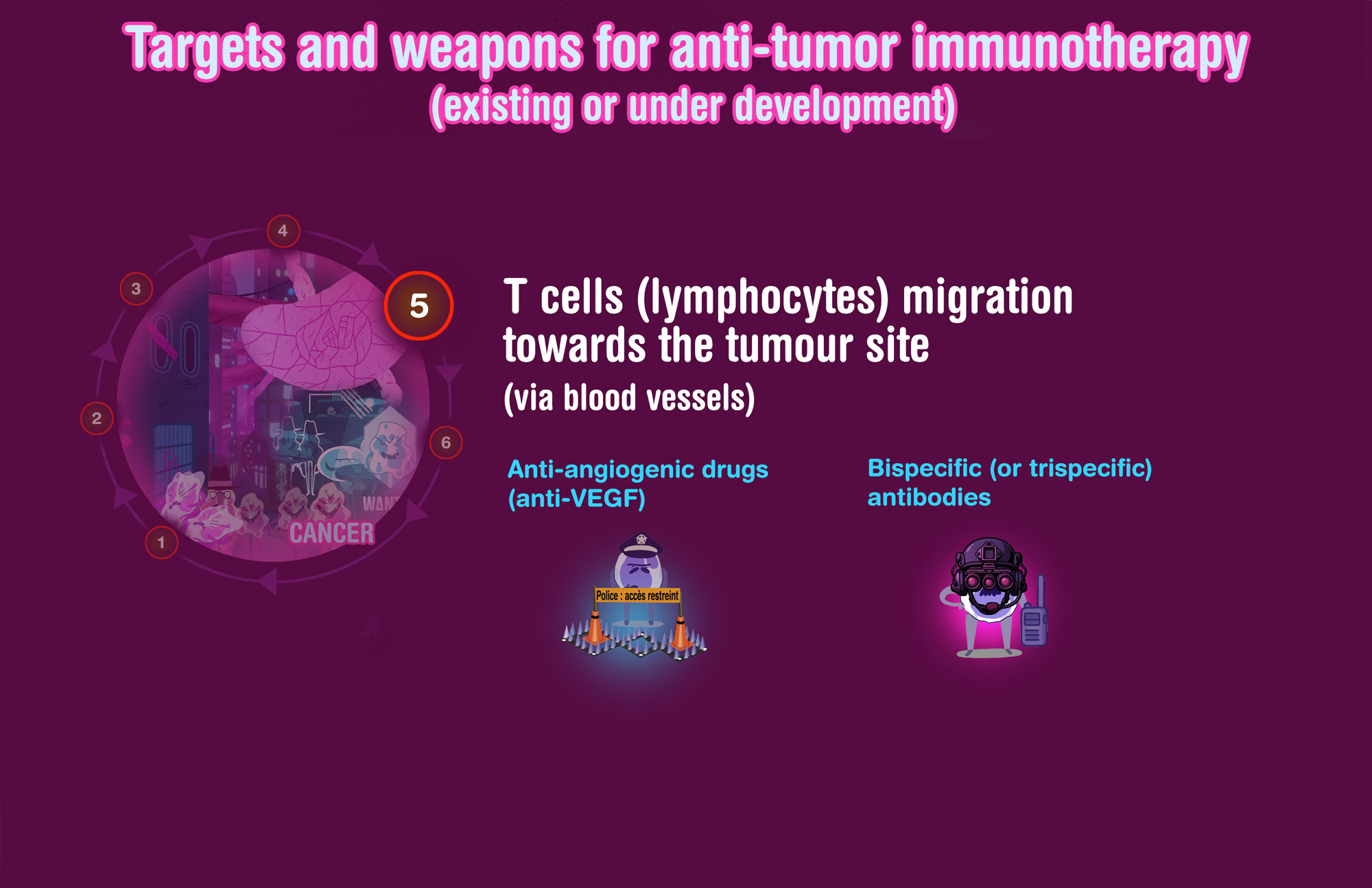
Available immunotherapies (and strategies)
Overview of anti-tumor immunotherapy treatments

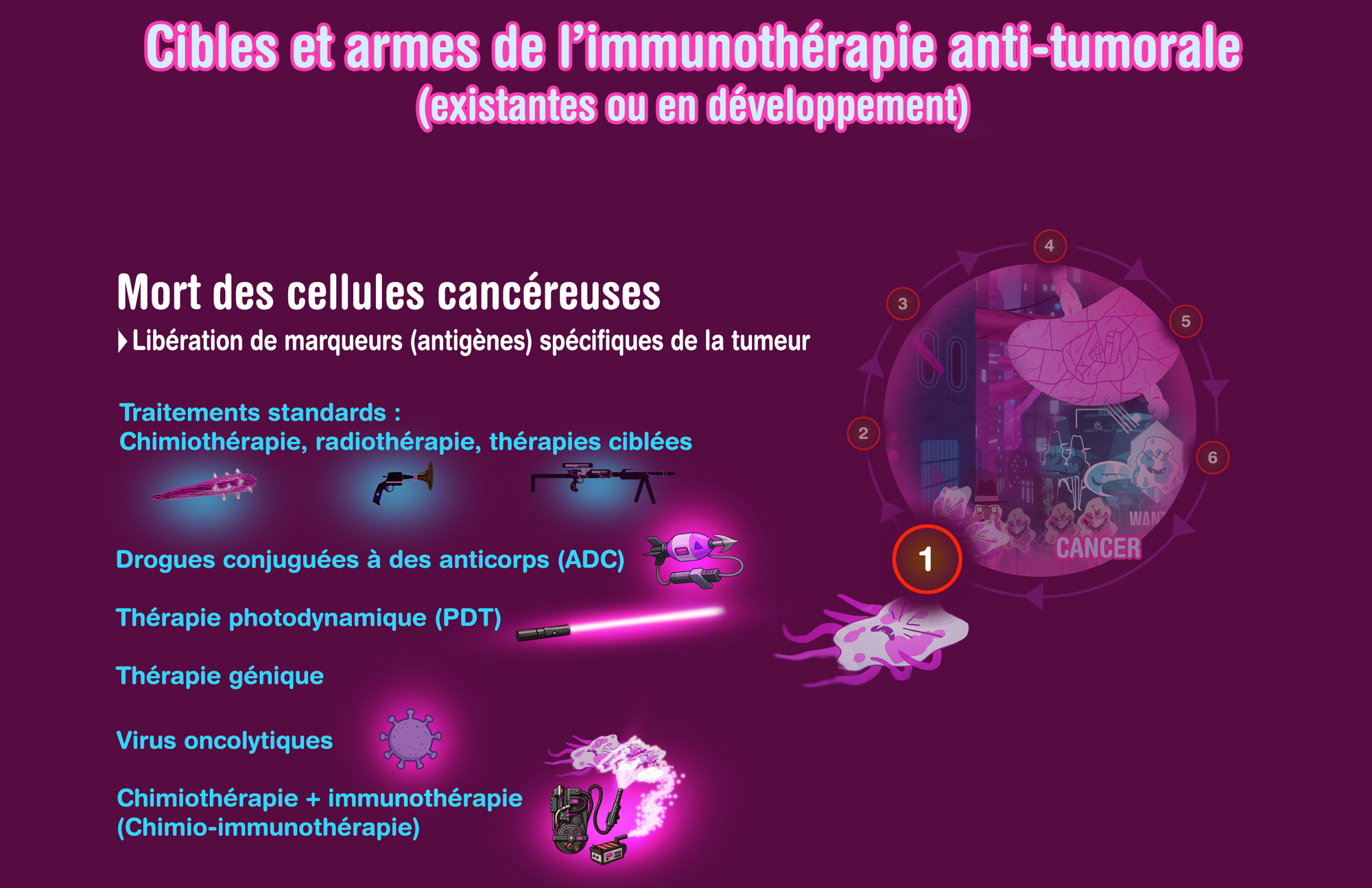
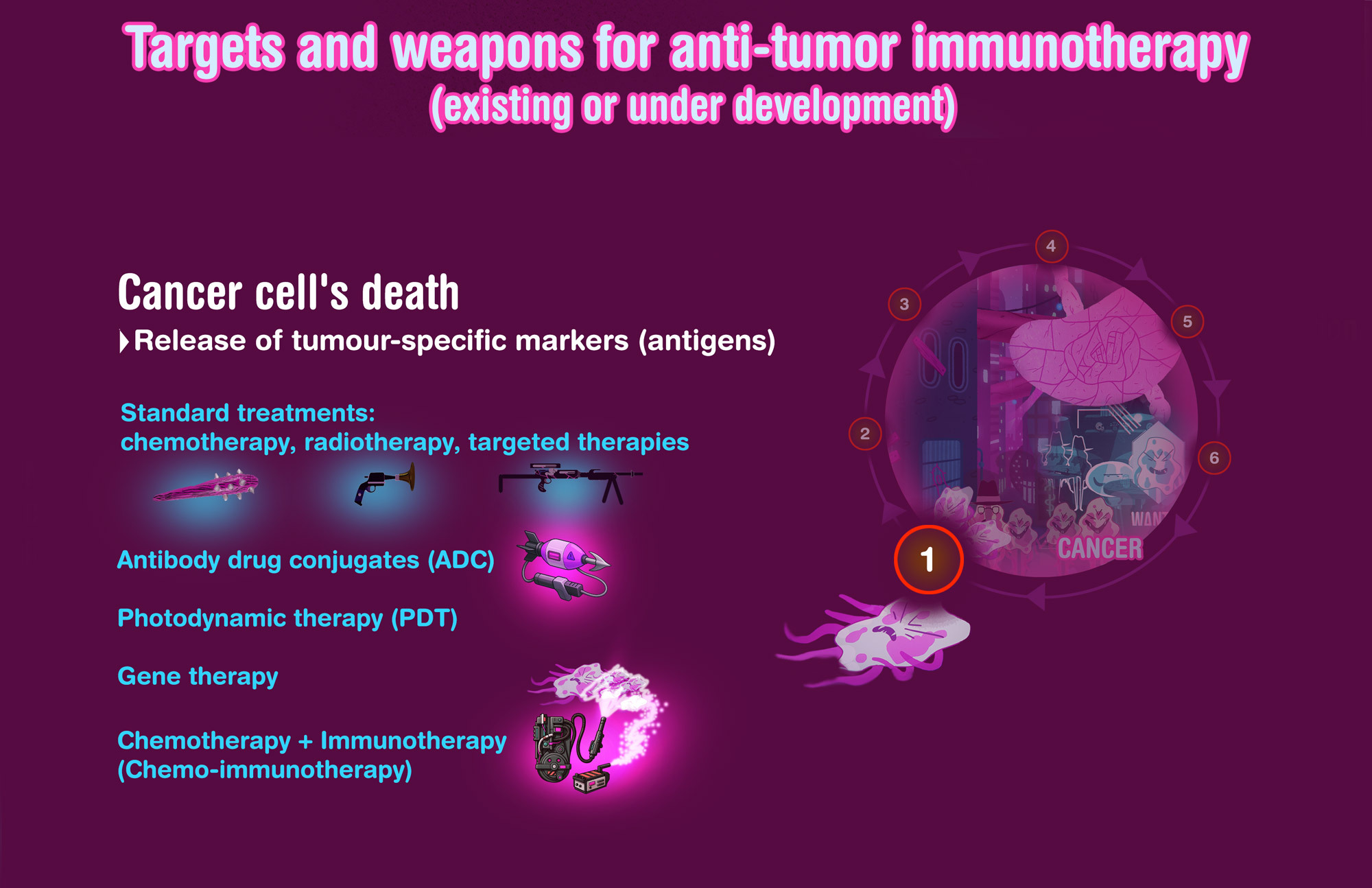
Chemotherapy + Immunotherapy (chemo-immunotherapy)
A new and major standard strategy, with synergistic anti-tumor effect of chemotherapy when combined with one or several immunotherapies

Bispecific (or trispecific) antibodies
Can target in the same time several immune checkpoints and/or other targets such as pro-angiogenic factor (VEGF) for example

Cell therapy
« Expert fighter » cells of the immune system, either issued from the patient but grown in large numbers and improved outside of the patient body (« ex vivo ») after sampling, or fully artificially produced with optimized cell surface receptors and molecules, before infusion to patient

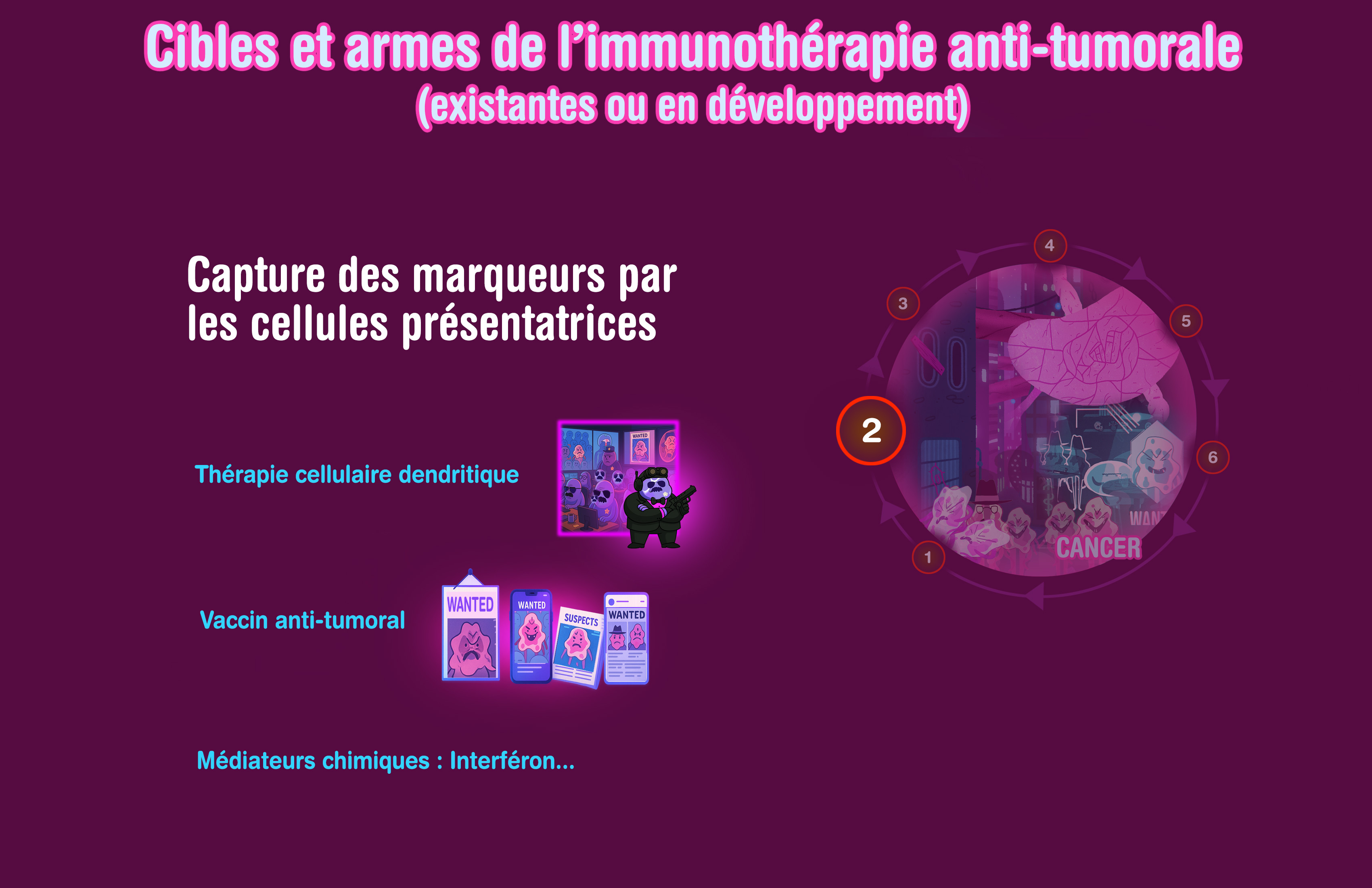
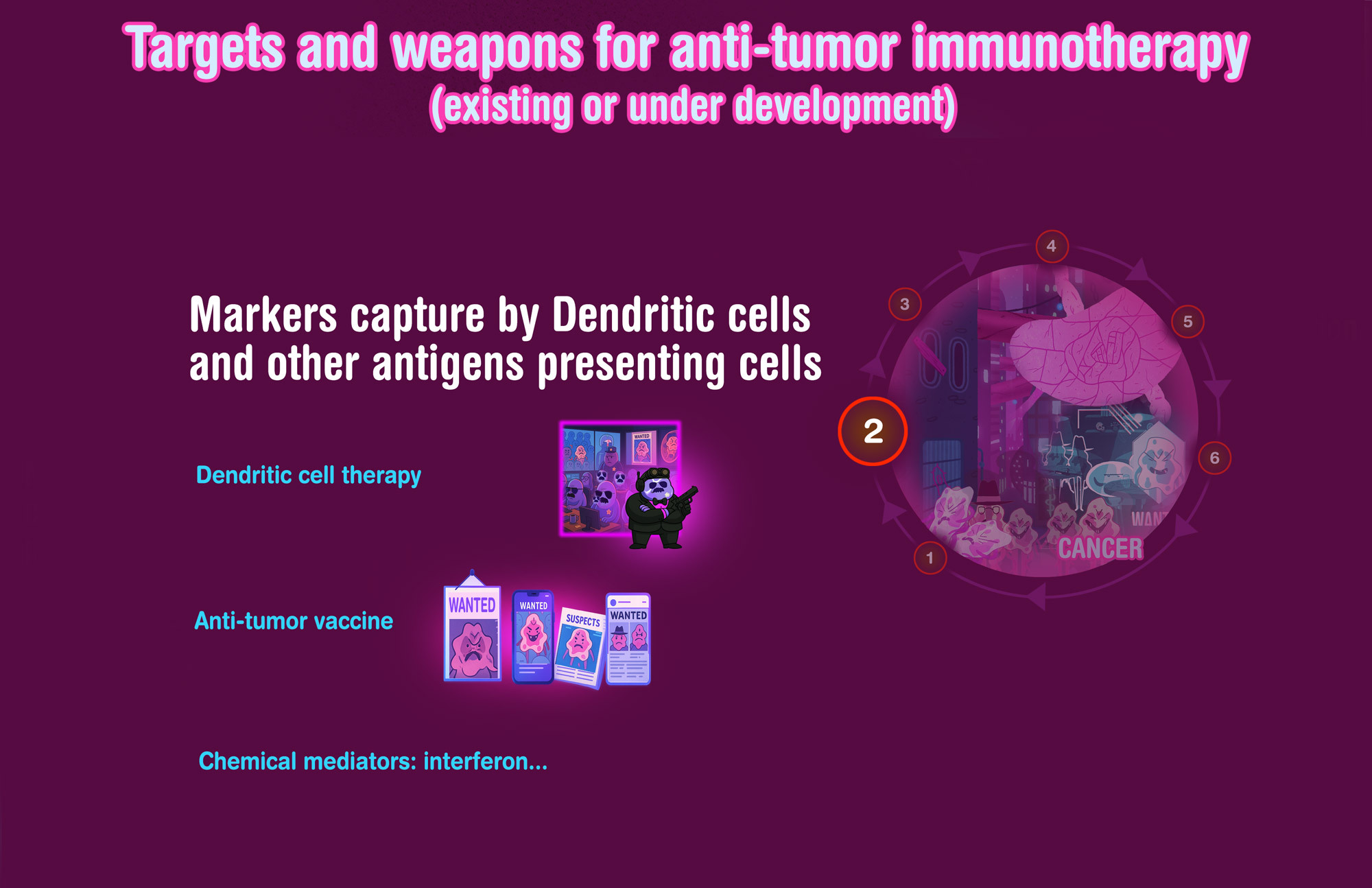
Dendritic cell therapy

Clonal Neoantigen Reactive T Cell
Tumor infiltrated lymphocytes (TILs)

CAR (chimeric antigen receptor) T cells

Anti-tumor Vaccine
With peptides, DNA, or rather messenger RNA currently, likely more efficient: to educate the immune system directly in the patient body, opposed to some other strategies (cell therapy…)
Bispecific T cell engaging antibodies (BiTE)
Antibodies « bridging » tumor cell and T cell, thus facilitating the engagement of the anti-tumor immune response
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADC)
Chemotherapy drugs vectorized by antibodies targeting tumor cells

Cytokines
Interferon, Interleukins: chemical messengers that can induce and/or facilitate an (anti-tumor) immune response

Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
Local treatment including first a systemic administration of photosensitizing drug, metabolized by tumor cells and reacting with light provided at a precise wavelength, and oxygen); PDT used alone or combined to immunotherapies to kill cancer cells and to facilitate anti-tumor immune response
Much many promising immunotherapies and multimodal strategies to come...
For example:
- • Oncolytic virus: virus with attenuated virulence, but which may induce anti-tumor immune response and/or directly kill cancer cells
- • Interventions on (gut) microbiota: treatments which may modulate the (gut) bacteria population to indirectly improve the efficiency of immunotherapies on anti-tumor immune response, and potentially decrease their toxicities